1️⃣ Intuition First
A unitary matrix represents a transformation that:
✔ Rotates or reflects vectors
✔ Does not stretch or shrink them
✔ Preserves total probability
Think of it like this:
A unitary operation moves a quantum state around in its space, but never distorts its length.
This is crucial because quantum states must always remain normalized.
2️⃣ Why Quantum States Must Be Preserved
A quantum state:
![]()
must satisfy:
![]()
If a transformation changed this length:
- probabilities would no longer sum to 1
- physics would break
👉 Unitary matrices are exactly the transformations that preserve length in complex vector spaces.
3️⃣ Formal Definition (Now the Math)
A matrix (U) is unitary if:
![]()
Where:
- (
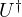 ) = conjugate transpose of (U)
) = conjugate transpose of (U) - (
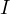 ) = identity matrix
) = identity matrix
Conjugate transpose means:
- Take the transpose
- Take complex conjugate of each entry
4️⃣ Simple Example (Hadamard Gate)
![]()
Compute:
![]()
So Hadamard is unitary.
What does it do?
![]()
It creates superposition without changing total probability.
5️⃣ Geometric Meaning (Very Important)

On the Bloch sphere:
- Unitary matrices correspond to rotations
- No stretching, no shrinking
- Every valid quantum gate is a rotation (or reflection)
📌 Key insight
Quantum computation is geometry in complex space.
6️⃣ What Unitary Is NOT
❌ Not any matrix
❌ Not allowed to scale vectors
❌ Not allowed to lose information
Example of non-unitary matrix:
![]()
This stretches vectors → invalid for quantum evolution.
7️⃣ Why All Quantum Gates Are Unitary
Quantum evolution follows Schrödinger’s equation, which guarantees:
✔ Reversibility
✔ Probability conservation
✔ Deterministic evolution before measurement
All of these imply:
![]()
8️⃣ Unitary Matrices in Quantum Machine Learning
Now connect this directly to QML.
Classical ML
![]()
- (
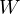 ): arbitrary matrix
): arbitrary matrix - Can shrink, expand, discard information
Quantum ML
![]()
- (
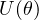 ): unitary
): unitary - Parameters (
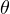 ) are trainable
) are trainable - No information loss until measurement
📌 Very important difference
Learning in QML happens under unitary constraints, not arbitrary linear maps.
9️⃣ Why Measurement Is Needed
Because unitary operations are:
- Linear
- Reversible
- Norm-preserving
They cannot:
- create nonlinearity
- discard information
👉 Measurement:
- collapses the state
- introduces nonlinearity
- produces classical outputs
This is why measurement plays the role of activation functions in QML.
10️⃣ One-Sentence Summary
A unitary matrix is a complex linear transformation that preserves vector length and probability, making it the only physically allowed operation for quantum evolution.
